ब्रेक एक ऐसा उपकरण है जिसके माध्यम ऐसा उपकरण है जिसके माध्यम से किसी भी चलती मशीन पर कृत्रिम प्रतिरोध लागू किया जाता है ताकि मशीन की गति धीमी या बंद हो सके |
The brake absorbs kinetic energy of moving member and convert it into the form of heat.
ब्रेक चलित सदस्य की सदस्य की kinetic energy को absorb करता है और इसे Heat के रूप में प्रसारित कर देता है|
Classification of Brakes :-
 |
| Classifcation of Brakes |
SOME BRAKE LINING MATERIALS :-
1. CAST IRON ON CAST IRON
2. BRONZE ON CAST IRON
3. STEEL ON CAST IRON.
4. LEATHER ON METAL
5. FIBER ON METAL
6. ABSETOS ON METAL
- PROPERTIES REQUIRED FOR A FRICTION LINING MATERIAL:-
* Higher coefficient of friction.
* Higher wear resistance.
* Higher thermal conductivity.
* Lower coefficient of thermal expansion.
* Good strength ( should able to withstand more load)
1 MECHANICAL BRAKES:-
which are operated by mechanical means such as liver ,spring, paddle .depending upon the shape of line friction materials.
TYPES:-
1. RADIAL BRAKES ( Internal and external Brakes)
2. ACXIAL BRAKES (Disk brakes)
2.HYDRAULIC AND PNEUMATIC BRAKES:-
Which are operated by fluid pressure such as oil pressure (hydraulic) and air pressure (pneumatic) .
3.ELECTRICAL BRAKES :-
Which are operated by magnetic force this type of brakes called electric or electrical brakes.
Example:- Hysteresis , age current brakes
- THE CAPACITY OF BRAKE DEPENDS UPON A FOLLOWING FACTORS :-
* The unit pressure between brake surface.
* The connecting area of breaking system.
* The radius of the drum.
* The coefficient of friction.
* The ability of the brake to desipate into the heat that is equalat to the energy being absorbed.
Mechanucal brake :- RADIAL BRAKES
Simple Internal and external brakes are called radial brake.
Types of radial brakes:-
1. BLOCK OR SHOE BRAKE :-
* SINGLE SHOE BRAKE
*PIVOTED BLOCK OR SHOE BRAKE
* DOUBLE BLOCK BRAKE
2.BAND BRAKE :-
*SINGLE BAND BRAKE
* DIFFERENTIAL BAND BRAKE
3.BAND + BLOCK BRAKE
Block or shoe brake

Single shoe brake:-
A single block or shoe brake consists of a block or shoe which is
Pressed against the rim of a revolving brake wheel drum. The block is made of a softer material than
the rim of the wheel. This type of a brake is commonly used on railway trains and tram cars. The
Friction between the block and the wheel causes a tangential braking force to act on the wheel, which
Retard the rotation of the wheel. The block is pressed against the wheel by a force applied to one end
of a lever to which the block is rigidly fixed. The other end of the lever is
Pivoted on a fixed fulcrum O.
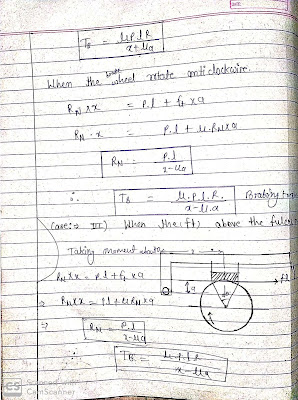
Let...
P = Force applied at the end of the lever,
RN = Normal force pressing the brake block on the wheel,
r = Radius of the wheel,
2θ = Angle of contact surface of the block,
µ = Coefficient of friction, and
Ft = Tangential braking force or the frictional force acting at the contact surface of the block and the wheel.
BAND BRAKE
SIMPLE BAND BRAKE:-
A band brake consists of a flexible band of leather, one or more ropes,or a steel lined with
friction material, which embraces a part of the circumference of the drum. A band brake, as shown in Fig. is called a simple band brake in which one end of the band is attached to a fixed pin or fulcrum of the lever while the other end is attached to the lever at a distance b from the fulcrum.
DIFFERENTIAL BAND BRAKE:-
In a differential band brake, as shown in Fig. , the ends of the band are joined at A and B to a lever AOC pivoted on a fixed pin or fulcrum O. It may be noted that for the band to tighten, the length OA must be greater than the length OB.







Comments
Post a Comment